Animating Images
| Image Animation is a continuous
display of a sequence of frames obtained from a given image. Each
frame represents the result displayed with a different amplitude. The
frames follow each other rapidly giving the feeling of
motion. By animating a deformed geometry or a normal vibration mode, you can get a better insight of the behavior of the system. Sometimes, you gain a more thorough understanding of the system behavior.
|
|||||||||
| This task shows how to Animate
Images.
|
|||||||||
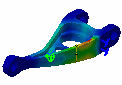
| You can use the sample26.CATAnalysis document:
you created a Stress Von Mises image.
Before You Begin:
|
|||||||||
1. Click the Animate icon
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||

|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
2. Click the
Pause button
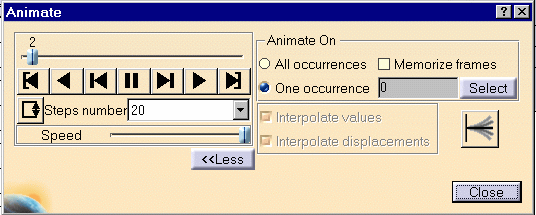
3. You can now change the animation parameters to the desired values:
For a smooth animation set the Number of steps parameter to its
maximum value (20) and activate the
Repeat play and reverse non stop button 4. Click the Play Forward button
|
|||||||||
| 5. If needed, modify the Steps
Number and click the More button.
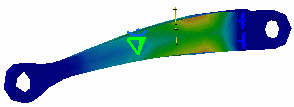
Both the the dialog box and the model appear as shown here:
If you select the symmetrical animation button
|
|||||||||
| 6. Click Close to leave
the Animate Window dialog box and thereby exit the Animation application.
|
|||||||||
| The animation capability is also available for Frequency
Solutions.
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||