|
This task shows the various methods for creating
helical
3D curves, such as coils and springs for example.
|
 |
Open the Helix1.CATPart
document.
|
 |
-
Click the Helix icon  . .
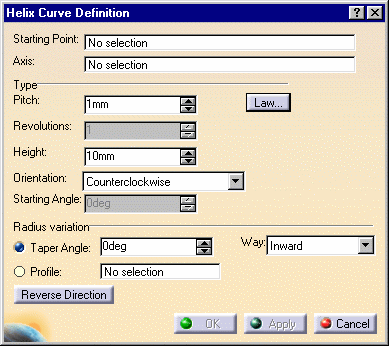
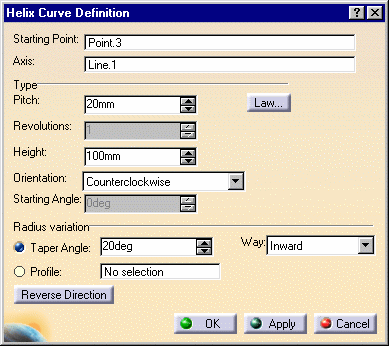
The Helix Curve Definition dialog box appears.
|
 |
|
-
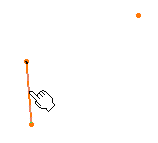
Select a starting point and an axis.
|
|
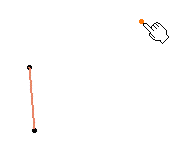 |
 |
|
-
Set the helix parameters:
|
|
 | Pitch: the distance
between two revolutions of the curve |
|
 |
|
You can define the evolution of the pitch along the
helix using a law.
|
|
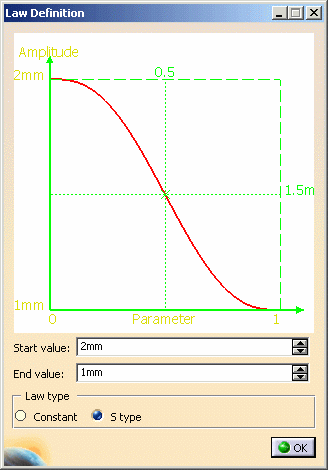
- Click the Law button to display the Law Definition dialog box.
- Choose type of law to be applied to the pitch: It can stay Constant,
or evolve according to a S
type law.
For the S type pitch, you need to define a second pitch value. The
pitch distance will vary between these two pitch values, over the
specified number of revolutions.
|
|
 |
-
The Law Viewer allows you to:
- visualize the law evolution and the maximum and minimum values,
- navigate into the viewer by panning and zooming (using to the
mouse),
- trace the law coordinates by using the manipulator,
- change the viewer size by changing the panel size
- reframe on by using the viewer contextual menu
- change the law evaluation step by using the viewer contextual menu
(from 0.1 (10 evaluations) to 0.001 (1000 evaluations)).
|
|
-
Click OK to return to the Helix Curve Definition
dialog box.
|
|
 | Height: the global height of the helical curve, in the
case of a constant pitch type helix
|
 | Orientation: defines the rotation direction (clockwise or
counter clockwise)
|
 | Starting Angle: defines where the helical curve starts,
in relation to the starting point.
This parameter can be set only for the Constant pitch only.
|
 | Taper Angle: the radius variation from one revolution
to the other. It ranges from -90° to 90° excluded.
For a constant radius, set the taper angle to 0.
|
 | Way: defines the taper angle orientation.
Inward: the radius decreases
Outward: the radius increases.
|
|
|
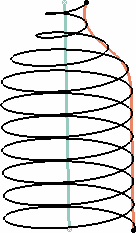
 | Profile: the curve used to control the helical curve
radius variation. The radius evolves according to the distance between
the axis and the selected profile (here the orange curve).
Note that the Starting point must be on the profile. |
|
|
|
 |
Starting Angle: defines where the helical curve starts,
in relation to the starting point.
This parameter can be set only for the Constant pitch only.
|
|
|
-
Click the Reverse Direction button to invert the curve direction.
|
|
-
Click OK to create the helix.
The helical curve (identified as Helix.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
|
 |

|